잘못된 내용은 언제든지 밑의 댓글로 알려주세요!
들어가기
앞선 Matrix Factorization 시리즈를 통해 ALS 알고리즘의 동작 과정을 살펴보았습니다. 이번 포스팅에서는 implict 라이브러리에 있는 ALS 패키지를 사용해보겠습니다. 또한 해당 포스팅은 이 글을 참조하여 작성했습니다.
1. 데이터 소개
이번 포스팅에서 사용한 데이터셋은 카카오 아레나 대회 데이터인 ‘멜론 플레이리스트’ 데이터 입니다. 우선 데이터셋을 간단하게 살펴보겠습니다.
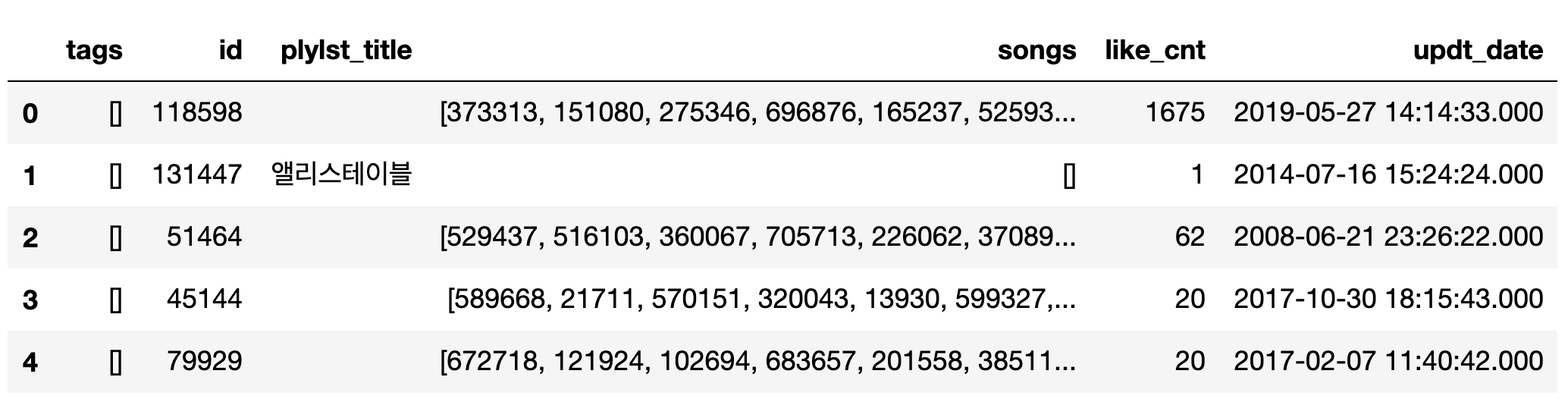
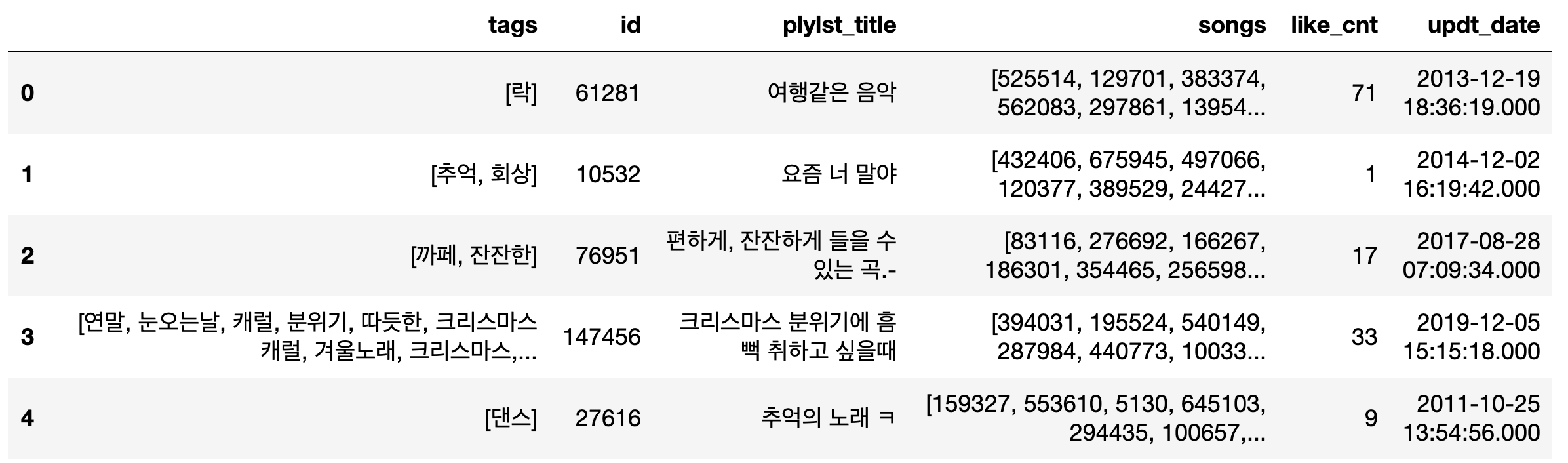
여기서 우리의 추천 목표는 각 playlist에 들어있는 100개의 곡과 10개의 태그를 맞추는 것입니다. 데이터 설명과 추천 과제는 카카오 아레나 홈페이지를 들어가시면 자세히 보실 수 있으니 설명은 하지 않겠습니다.
위 데이터셋에서 특이한 점은 songs column과 tags column의 데이터 값들이 list로 들어가있다는 점입니다. list type은 Matrix로 만들 수 없기 때문에 이 list 타입을 분해하는 것으로 데이터 전처리를 시작하겠습니다.
2. 데이터 전처리
이제 위 데이터 프레임에서 Songs와 tags만을 뽑아내어 해당 컬럼 내 list 값을 분해한 후 새로운 Matrix를 만들어 보겠습니다.
2.1 songs, tags 컬럼 list 변환
list 변환을 위해 df.tolist()명령어를 사용해 줍니다.
1
2
3
4
5
tr_songs = tr.songs.tolist()
te_songs = te.songs.tolist()
tr_tags = tr.tags.tolist()
te_tags = te.tags.tolist()
te_ids = te.id.tolist()
2.2 songs, tags 컬럼 id 초기화
이후 새로운 Matrix를 만들기 위해 songs와 tags의 id를 초기화해 줍니다. 여기서 나중에 join을 없애기 위해 새롭게 초기화된 songs와 tags를 dictionary 형태로 담아줍니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
from itertools import groupby
tr = [] # tr 초기화
iid_to_idx = {} # iid_to_idx : songs의 id들이 들어있는 곳
tag_to_idx = {} # tag_to_idx : tags의 id들이 들어있는 곳
idx = 0
# songs id 초기화
for i, l in enumerate(tr_songs):
view = l
for item_id in view:
if item_id not in iid_to_idx:
iid_to_idx[item_id] = idx
idx += 1
view = [iid_to_idx[x] for x in view]
tr.append(view) # => song_id 재설정
n_items = len(iid_to_idx) # 615142
# tags id 초기화
idx = 0
for i, tags in enumerate(tr_tags):
for tag in tags:
if tag not in tag_to_idx:
tag_to_idx[tag] = n_items + idx
idx += 1 # => tags_id 설정
tr[i].extend([tag_to_idx[x] for x in tags]) # tr[i] => 'i'th row의 songs_list + tags_list
n_tags = len(tag_to_idx) # 29160
위의 코드를 실행시킨 뒤 iid_to_idx의 dictionary 형태를 살펴보면 {song_id : new initialize index}로 song_id가 키값으로 들어가 있습니다. 따라서 song_id가 value값이 되도록 dictionary의 순서를 바꿔줍니다. 이는 tag_to_idx에서도 마찬가지 입니다.
1
2
idx_to_iid = {x:y for(y,x) in iid_to_idx.items()}
idx_to_tag = {(x - n_items):y for(y,x) in tag_to_idx.items()}
2.3 Implicit Matrix 생성
이제 Implicit Matrix를 만들 차례입니다. 이를 위해 csr_matrix의 함수에 대해 먼저 알아보겠습니다.
2.3.1. csr_matrix 함수
csr_matrix는 scipy의 내장 함수 중 하나입니다. csr_matrix는 보통 sparce matrix와 함께 사용됩니다. 그 이유는 sparce matrix의 대부분의 값들이 0 혹은 비어있는 값입니다. 그렇기에 sparce matrix를 데이터프레임이나 일반 Matrix로 저장하면 메모리 효율도 낮고, 속도도 느립니다. 따라서 이런 문제를 csr_matrix를 이용해 해결합니다. 예시를 보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
rows = [0, 0, 1, 1, 3, 3]
cols = [0, 4, 1, 3, 0, 3]
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
csr = csr_matrix((data, (rows, cols)), shape = (max(rows)+1, max(cols) + 1))
csr.todense()
matrix([[1, 0, 0, 0, 2],
[0, 3, 0, 4, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[5, 0, 0, 6, 0]], dtype=int64)
위의 Matrix에서 볼 수 있듯이 data의 i번째 원소는 (rows[i], cols[i])의 인덱스를 가지고, 이에 따라 Matrix의 차원은 rows는 0부터 3까지므로 4차원, cols는 0부터 4까지이므로 5차원으로 설정할 수 있습니다. 여기서 csr_matrix의 shape를 설정할 때 항상 위의 shape보다 크거나 같게 설정해야 합니다.
그럼 이제 다시 본 코드로 돌아가겠습니다.
우리는 앞서 song_id와 tag_id를 초기화시켰습니다. 초기화를 시킨 이유는 바로 id 값이 sparce matrix의 column_index로 들어가기 때문입니다. 또 ALS를 사용하기 위해서는 앞선 포스팅에서 값이 있으면 1, 없으면 0으로 만들어주어야 한다고 언급한바 있습니다. 따라서 csr_matrix를 만드는 함수는 다음과 같이 짜여질 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
def lil_to_csr_matrix(lil, shape = None):
row = []
col = []
for row_idx,list_element in enumerate(lil):
for j, col_idx in enumerate(list_element):
row.append(row_idx)
col.append(col_idx)
# lil 데이터를 첫 행부터 차례대로 불러와 그 개수만큼 1을 채워넣는 함수
data = np.repeat(1, sum([len(x) for x in lil]))
# row는 lil 데이터에서 불러온 값의 row와 똑같고, col은 초기화시킨 songs or tags의 id값
return csr_matrix((data, (row,col)), shape = shape)
이후 train데이터와 test 데이터 모두 csr_matrix로 변형시켜 줍니다.
1
2
3
4
# n_items : 615142
# n_tags : 29160
tr_csr_mat = lil_to_csr_matrix(tr, (len(tr), n_items + n_tags)) #115071x644302
te_csr_mat = lil_to_csr_matrix(te, (len(te), n_items + n_tags)) #23015x644302
2.4 ALS 모델 생성
crs_matrix 함수를 이용해 implicit 데이터셋을 값이 있는 부분은 1, 없는 부분은 0인 sparce matrix로 만드는 작업이 끝났습니다. 이제 ALS 모델을 생성하고 학습시켜 보겠습니다.
ALS 모델을 만들기 위해 우리는 \(N_f\)와 regularization을 위한 \(\lambda\)값을 설정해주어야 합니다. 또한 ALS의 fit 함수는 (item, user)의 차원으로 데이터셋을 입력받으므로 현재 (plylist, songs or tags), 즉 (user, item)으로 되어 있는 데이터셋을 전치주어야 합니다.
1
2
3
# ALS 모델 생성
als_model = ALS(factors=128, regularization=0.08)
als_model.fit(tr_csr_mat.T * 15.0)
여기에 우리는 songs와 tags를 각각 100개, 10개씩 추천해주어야 하므로 위의 ALS 모델을 songs 추천모델과 tags 추천모델로 구분해줍니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
song_model = ALS(use_gpu=False)
tag_model = ALS(use_gpu=False)
# item_factor, user_factor = Array of latent factors for each item in the training set
song_model.user_factors = als_model.user_factors
tag_model.user_factors = als_model.user_factors
# index slicing을 통해 tag와 item을 구분해줍니다.
song_model.item_factors = als_model.item_factors[:n_items]
tag_model.item_factors = als_model.item_factors[n_items:]
2.4 ALS 모델을 통한 추천 결과 추출
ALS 모델에서 추천을 위해서는 recommend 함수를 사용해야 합니다. 모델에 데이터를 넣기 위해 id 초기화 과정에서 합쳐진 songs와 tags 데이터를 다시 분리하여 모델에 넣어줍니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# train 데이터 분리
song_rec_csr = tr_csr_mat[:, :n_items] #shape = (115071, 615142)
tag_rec_csr = tr_csr_mat[:, n_items:] #shape = (115071, 29160)
song_ret = []
tag_ret = []
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
for plylis_id in tqdm(range(te_csr.shape[0])):
# 100개의 song 추천이므로 N=100
song_rec = song_model.recommend(plylis_id, song_rec_csr, N=100)
# change song column index to original song_id
song_rec = [idx_to_iid[x[0]] for x in song_rec]
# 10개의 tag 추천이므로 N=10
tag_rec = tag_model.recommend(u, tag_rec_csr, N=10)
# change tag column index to original tag_id
tag_rec = [idx_to_tag[x[0]] for x in tag_rec if x[0] in idx_to_tag]
song_ret.append(song_rec)
tag_ret.append(tag_rec)
위의 코드를 통해 100개의 노래와 10개의 태그를 추출했습니다. 여기서 중요한 것은 처음 song_rec를 통해 나오는 값들은 column index로 쓰기 위해 초기화된 id 값입니다.
이를 처음에 만들었던 song-id dictionary에 넣어주어야 원래의 song_id를 추출할 수 있습니다. 이는 tag에서도 마찬가지 입니다.
3. 전체 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
from implicit.evaluation import *
from implicit.als import AlternatingLeastSquares as ALS
from implicit.bpr import BayesianPersonalizedRanking as BPR
import numpy as np
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from scipy.sparse import *
import scipy
import pandas as pd
tr = pd.read_json("./train.json", encoding="utf-8")
te = pd.read_json("./val.json", encoding="utf-8")
# tr.tags의 모든 List 데이터를 분해하는 과정
# list 더하기 연산 살펴보기
# https://wikidocs.net/14
# np.concatenate(tr.tags, axis = None)과 같은 결과
ret = []
for tag in tr.tags.tolist():
ret += tag
# tr내 tag별 사용된 횟수를 구하는 코드
# dict 명령어를 사용하여 counter type을 dict 타입으로 변환
from collections import Counter
r = dict(Counter(ret))
r = sorted(r.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])
# songs, tags list
top_tags = [x[0] for x in r[:1000]] # for문을 List로 한번에 출력하는 방법
tr_songs = tr.songs.tolist()
te_songs = te.songs.tolist()
tr_tags = tr.tags.tolist()
te_tags = te.tags.tolist()
te_ids = te.id.tolist()
# tr.song id 초기화
from itertools import groupby
tr = [] # tr 초기화
iid_to_idx = {} # iid_to_idx : songs의 id들이 들어있는 곳
tag_to_idx = {} # tag_to_idx : tags의 id들이 들어있는 곳
idx = 0
for i, l in enumerate(tr_songs):
view = l
for item_id in view:
if item_id not in iid_to_idx:
iid_to_idx[item_id] = idx
idx += 1
view = [iid_to_idx[x] for x in view]
tr.append(view) # => song_id 재설정
n_items = len(iid_to_idx)
# tr.tags id 초기화
idx = 0
for i, tags in enumerate(tr_tags):
for tag in tags:
if tag not in tag_to_idx:
tag_to_idx[tag] = n_items + idx
idx += 1 # => tags_id 설정
tr[i].extend([tag_to_idx[x] for x in tags]) # tr[i] => 'i'th row의 songs_list + tags_list
n_tags = len(tag_to_idx)
# test set도 train set과 같은 process 진행
from itertools import groupby
te = []
idx = 0
for i, l in enumerate(te_songs):
view = l
ret = []
for item_id in view:
if item_id not in iid_to_idx:
continue
ret.append(iid_to_idx[item_id])
te.append(ret)
idx = 0
for i, tags in enumerate(te_tags):
ret = []
for tag in tags:
if tag not in tag_to_idx:
continue
ret.append(tag)
te[i].extend([tag_to_idx[x] for x in ret])
# tr shape = (len(원 데이터 플레이리스트), max(list(map(lambda x : len(x), tr))))
tr = shuffle(tr)
# raw data와 매칭시키기 위해 dictionary에 저장
# y= song, x = id
idx_to_iid = {x:y for(y,x) in iid_to_idx.items()}
idx_to_tag = {(x - n_items):y for(y,x) in tag_to_idx.items()}
# make csr_matrix
def lil_to_csr_matrix(lil, shape = None):
row = []
col = []
for row_idx,list_element in enumerate(lil):
for j, col_idx in enumerate(list_element):
row.append(row_idx)
col.append(col_idx)
data = np.repeat(1, sum([len(x) for x in lil]))
return csr_matrix((data, (row,col)), shape = shape)
# n_items : 615142
# n_tags : 29160
tr_csr_mat = lil_to_csr_matrix(tr, (len(tr), n_items + n_tags)) #115071x644302
te_csr_mat = lil_to_csr_matrix(te, (len(te), n_items + n_tags)) #23015x644302
# ALS 모델 생성
als_model = ALS(factors=128, regularization=0.08, calculate_training_loss = True)
als_model.fit(tr_csr_mat.T * 15.0)
item_model = ALS(use_gpu=False)
tag_model = ALS(use_gpu=False)
item_model.user_factors = als_model.user_factors
tag_model.user_factors = als_model.user_factors
item_model.item_factors = als_model.item_factors[:n_items]
tag_model.item_factors = als_model.item_factors[n_items:]
# tr_csr_mat에서 plylist 행은 그래도 유지하고 songs matrix와 tags matrix로 분리
item_rec_csr = tr_csr_mat[:, :n_items] #shape = (115071, 615142)
tag_rec_csr = tr_csr_mat[:, n_items:] #shape = (115071, 29160)
# item_model.recommend(u, item_rec_csr, N=100)
# u = Userid 그래서 te_csr_mat.shape[0]으로 앞의 plylist id만 가져옴
# N = number of results to return => N = 100 : 100개를 추천값으로 돌려줌
# item_rec_csr : sparse matrix of shape(number_users, number_items) train 데이터를 넣어야 한다.
item_ret = []
tag_ret = []
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
# recommendation for each plylist
for plylist_id in tqdm(range(te_csr_mat.shape[0])):
# item recommedation
item_rec = item_model.recommend(plylist_id, item_rec_csr, N=100)
# item_rec 출력 형태 : [(3783, 0.7968637), (2663, 0.68133116)]
# 이거를 하나하나씩 x에 넣음 => (3783, 0.7968637) 넣은 후 (2663, 0.68133116)
# x[0]을 통해 songs_id를 출력
# idx_to_iid[x[0]] = idx_to_iid[songs_id] => songs value 출력
item_rec = [idx_to_iid[x[0]] for x in item_rec]
# tag recommendation
tag_rec = tag_model.recommend(u, tag_rec_csr, N=10)
tag_rec = [idx_to_tag[x[0]] for x in tag_rec if x[0] in idx_to_tag]
# input recommendation result into empty list
item_ret.append(item_rec)
tag_ret.append(tag_rec)
# 결과 출력
returnval = []
for _id, rec, tag_rec in zip(te_ids, item_ret, tag_ret):
returnval.append({
"id": _id,
"songs": rec[:100],
"tags": tag_rec[:10]
})
import json
with open('results.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(returnval, ensure_ascii=False))
reference
- 카카오 아레나 포럼
- https://implicit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/als.html
- https://lovit.github.io/nlp/machine%20learning/2018/04/09/sparse_mtarix_handling/